The advent of 5G technology has been a significant leap forward in wireless communication, and millimeter wave antennas stand as a cornerstone of this evolution. As the global 5G millimeter wave industry gears up for expansion, the question arises: what does the future hold for millimeter wave technology?
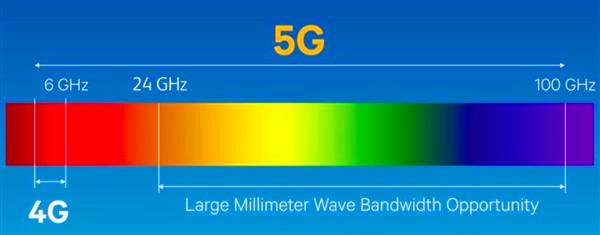
The Dual Frequency Bands of 5GThe 3GPP standards body defines two primary frequency bands for 5G antennas: the FR1 band (450MHz to 6GHz), also known as Sub-6GHz, and the FR2 band (24.25GHz to 52.6GHz), commonly referred to as millimeter wave. While Sub-6GHz serves as the foundational coverage network for 5G, millimeter wave antenna is poised to become a critical component, filling in the gaps and enhancing the user experience by complementing Sub-6GHz technology.
The Dual-Edged Sword of Millimeter Wave CoverageDespite its shorter propagation distance, millimeter wave technology offers several compelling advantages:
Spectrum Abundance: Millimeter wave provides a wealth of spectrum resources, translating to higher potential data rates for users.
Low Latency: The technology is inherently capable of lower communication delays.
Compact Design: Millimeter wave antennas are smaller and lighter, facilitating easier deployment and scalability.
High Precision: The point-to-point communication nature of millimeter waves allows for superior positioning accuracy compared to Sub-6GHz.
Line-of-Sight and BeyondMillimeter wave propagation relies on both line-of-sight and non-line-of-sight methods. While millimeter waves are more susceptible to blockage and have higher propagation loss, this characteristic can be harnessed for controlled coverage. This feature is advantageous for creating isolated coverage zones within a network, enabling customized configurations such as prioritizing uplink in certain areas and downlink in others.However, the limited coverage area of millimeter wave signals poses a challenge for widespread 2C user service. To achieve continuous coverage akin to Sub-6GHz, a denser network of base stations is required, making millimeter wave technology more suitable for hotspot areas in combination with Sub-6GHz networks.
The Promising Outlook for Millimeter Wave ApplicationsMillimeter wave technology is not just promising; it's set to revolutionize various sectors. Although currently in the nascent stages of 5G, with limited applications and an unclear market space, millimeter wave is expected to become an indispensable choice in the later stages of 5G evolution.The technology's rich spectrum and vast potential are anticipated to significantly expand the service capabilities of 5G systems, meeting the escalating demand for data traffic and fostering innovation across vertical industries. This advancement is expected to drive the digital transformation of society at large.
Economic Impact of 5G Millimeter WaveAccording to GSMA, 5G millimeter wave is projected to be a key driver in sectors like high-speed access, industrial automation, healthcare, intelligent transportation, and virtual reality, contributing an estimated US$565 billion to the global GDP by 2035. This accounts for 25% of the total 5G contribution. Furthermore, the economic benefits of 5G millimeter wave frequency band usage in China alone are projected to reach approximately US$104 billion before 2034.
As we stand on the brink of a new era in wireless communication, 5G millimeter wave antennas are set to play a pivotal role. Their ability to enhance data rates, reduce latency, and enable precise communication positions them as a critical component of 5G's success. Despite the challenges, the future looks bright for millimeter wave technology, with the potential to not only meet but exceed the growing demands of our increasingly connected world.
TAG:The Future Potential of 5G with Millimeter Wave Antennas https://www.rfelement.com



